Hello, I’m Mana.
Today, I’d like to explain one of the core technologies behind generative AI: the Large Language Model (LLM), in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini and many other generative AI tools are all powered by this LLM technology.
🔠 What Is a Language Model?
A language model is a model designed to predict the next word (or character) in a sentence.
Example: “Today, I went to the cafe and had a ( )”
→ The model might predict: “coffee,” “latte,” or “drink.”
To make such predictions accurately, LLMs are trained on large volumes of text data.
🧠 Basic Structure of an LLM
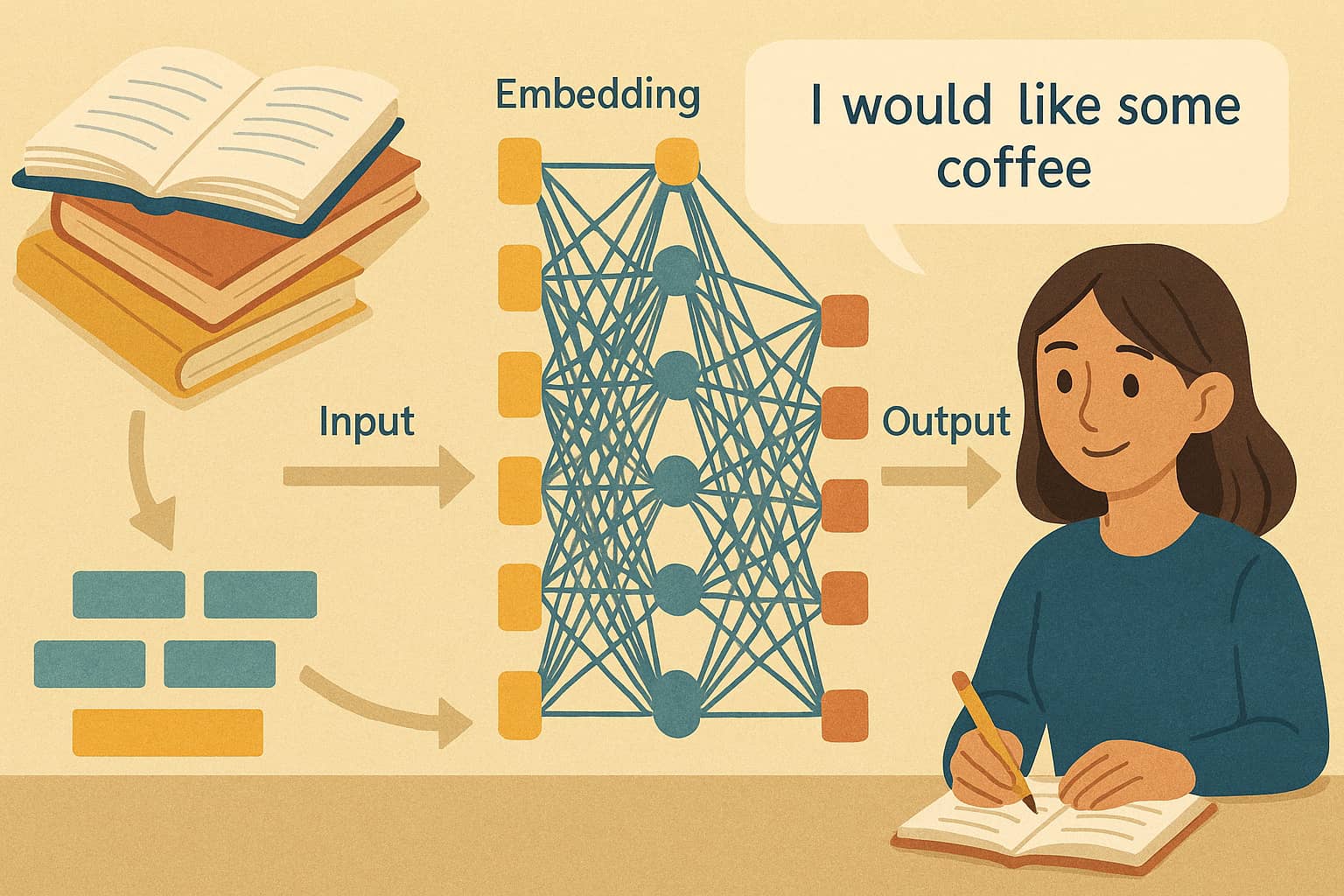
Most LLMs are based on an architecture called the Transformer.
Main Components:
- Tokenization: Splitting text into small units (“tokens”)
- Embedding: Converting tokens into vectors (numerical data)
- Self-Attention Mechanism: Capturing important relationships within the text
- Multi-Layer Structure: Processing and abstracting information over many layers
🔍 Detailed Examples
Tokenization: A sentence like “I use ChatGPT every day” would be tokenized into parts like [“I”, “use”, “Chat”, “G”, “PT”, “every”, “day”]. This lets the AI better understand language structures.
Embedding: Tokens are turned into vectors. Words with similar meanings will have similar vector representations:
“coffee” → [0.81, 0.23, -0.10, …]
“tea” → [0.78, 0.25, -0.12, …]
“car” → [0.05, -0.91, 0.88, …]
Self-Attention: In a sentence like “Taro gave Hanako a gift. She was very happy,” the model can understand that “she” refers to “Hanako” by using attention scores between words.
Multi-Layer Network: Each layer extracts more abstract information, like how a human builds understanding step by step:
1. Word-level meaning
2. Sentence structure
3. Context across multiple sentences
4. Output generation with natural flow
The deeper the layers, the more abstract the AI’s understanding becomes.
These components work together to help the model produce natural, context-aware responses.
📚 How an LLM Learns
① Pre-training
- Trained on massive datasets from the internet
- Learns grammar, context, and general knowledge
- Often learns through fill-in-the-blank tasks
② Fine-tuning
- Tailored for specific tasks like conversation, translation, or summarization
③ Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF)
- Uses human ratings to align output with human expectations
- Helps improve politeness, safety, and helpfulness
📘 Final Thoughts
Large Language Models (LLMs) are the engine behind today’s generative AI tools. Understanding how they work—from tokenization and embeddings to multi-layer reasoning—can help you make better use of these tools and think more critically about their capabilities and limitations.
Let’s keep learning together! 📘


Comment