When taking the Japanese Hazardous Materials Handler Examination, it is essential to understand the concept of specified quantities and how to calculate their ratios accurately. Specified quantities refer to the amounts set by the Fire Service Act for different types of hazardous materials. If these amounts are exceeded, special regulations and handling are required. This article explains the calculation method for specified quantity ratios and their importance in the examination.
Basic Concept of Specified Quantities
Specified quantities are set under Article 10 of the Fire Service Act and are determined based on the danger of particular hazardous materials. If hazardous materials are stored or handled in amounts exceeding these specified quantities, it is legally required to have appropriate facilities and equipment.
Specified Quantities for Class 4 Hazardous Materials
For example, the specified quantity for gasoline (Class 1 petroleum product) is 200 liters. This means that if you store more than 200 liters of gasoline, a special storage facility is required.
Below is a table showing the specified quantities for Class 4 hazardous materials. Make sure to memorize these quantities.
| Name | Properties | Examples | Specified Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Special Inflammable Material | - | Carbon Disulfide | 50L |
| Class 1 Petroleum | Non-aqueous Liquid | Gasoline | 200L |
| Aqueous Liquid | Acetone | 400L | |
| Alcohol | - | Ethanol | 400L |
| Class 2 Petroleum | Non-aqueous Liquid | Kerosene | 1,000L |
| Aqueous Liquid | 1-Butanol | 2,000L | |
| Class 3 Petroleum | Non-aqueous Liquid | Heavy Oil | 2,000L |
| Aqueous Liquid | Glycerin | 4,000L | |
| Class 4 Petroleum | - | Gear Oil | 6,000L |
| Animal and Vegetable Oils | - | Soybean Oil | 10,000L |
Calculation Method for Specified Quantity Ratios
Calculating specified quantity ratios is a frequently tested topic in the Japanese Hazardous Materials Handler Examination. Article 10, Section 2 of the Fire Service Act stipulates how to calculate specified quantities when storing or handling multiple types of hazardous materials at the same location.
Steps to Calculate the Specified Quantity Ratios
To calculate the specified quantity ratio for a single type of hazardous material, divide the amount stored or handled by the specified quantity for that material.
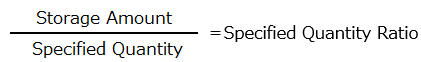
When storing or handling multiple types of hazardous materials at the same location, sum the values obtained by dividing the amount of each hazardous material by its specified quantity. The total is the specified quantity ratio.
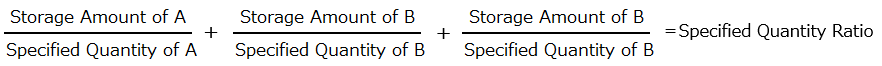
If the total is 1 or more, the location is considered to be storing or handling hazardous materials in quantities that exceed the specified limits.
Examples
Here are some concrete examples:
- Gasoline (specified quantity 200 liters) – 150 liters
- Kerosene (specified quantity 1,000 liters) – 300 liters
In this case, the specified quantity ratio is calculated as follows:
Gasoline: 150 liters ÷ 200 liters = 0.75
Kerosene: 300 liters ÷ 1,000 liters = 0.30
Summing these values, 0.75 + 0.30 = 1.05, which is 1 or more. Therefore, a special storage facility is required in this case.
Handling of Specified Quantities in the Examination
The Japanese Hazardous Materials Handler Examination frequently includes questions on specified quantities. Examinees must memorize the specified quantities for each hazardous material and understand the calculation method for ratios when multiple hazardous materials are handled at the same location.
Exam Preparation Tips
- Memorize Specified Quantities: It is crucial to accurately memorize the specified quantities for major hazardous materials.
- Practice Calculations: Understand the calculation methods and practice, as the patterns are limited.
Example Exam Question 1
ガソリン(第1石油類)200Lと灯油(第2石油類)2,000Lとを同一の場所で貯蔵する場合の指定数量の倍数について次のうち正しいのはどれか?
If gasoline (Class 1 petroleum product) 200L and kerosene (Class 2 petroleum product) 2,000L are stored at the same location, what is the correct specified quantity ratio?
(1) 2 times
(2) 3 times
(3) 4 times
(4) 5 times
(5) 6 times
Explanation
The specified quantity ratio is calculated by summing the values obtained by dividing the amount of each hazardous material by its specified quantity.
The specified quantities for each hazardous material are as follows:
- Gasoline (Class 1 petroleum product): 200 liters
- Kerosene (Class 2 petroleum product): 1,000 liters
Ratio Calculation
- Gasoline: 200 liters ÷ 200 liters = 1
- Kerosene: 2,000 liters ÷ 1,000 liters = 2
Summing these values: 1 + 2 = 3
Therefore, the specified quantity ratio is 3 times. Check the answer options.
Answer: (2)
Example Exam Question 2
ある貯蔵倉庫にアセトン600L、灯油3,000L、重油6,000Lを貯蔵している場合、この貯蔵所は指定数量の何倍を貯蔵していることになるか?
If a storage warehouse contains 600L of acetone, 3,000L of kerosene, and 6,000L of heavy oil, what is the specified quantity ratio for this storage location?
(1) 4.0 times
(2) 5.5 times
(3) 6.0 times
(4) 7.5 times
(5) 9.0 times
Explanation
As with the previous question, calculate the specified quantity ratio by dividing the amount of each hazardous material by its specified quantity and summing the values.
Specified Quantities
- Acetone (Class 4 hazardous material, Class 1 petroleum): 400 liters
- Kerosene (Class 4 hazardous material, Class 2 petroleum): 1,000 liters
- Heavy oil (Class 4 hazardous material, Class 3 petroleum): 2,000 liters
Ratio Calculation
- Acetone: 600 liters ÷ 400 liters = 1.5
- Kerosene: 3,000 liters ÷ 1,000 liters = 3.0
- Heavy oil: 6,000 liters ÷ 2,000 liters = 3.0
Summing these values: 1.5 + 3.0 + 3.0 = 7.5
Therefore, this storage location has a specified quantity ratio of 7.5 times.
Answer: (4)
Conclusion
Calculating specified quantity ratios is a crucial concept under the Fire Service Act and is frequently tested in the Japanese Hazardous Materials Handler Examination. Gaining accurate knowledge and calculation skills will help you pass the exam and ensure safe handling of hazardous materials in your work. We hope this article helps you understand specified quantities and prepare for the examination.



コメント